In this post we will configure SAP S4 HANA Logistics Execution Organization Structure. we will also see in brief what is changed in S4 HANA compared to traditional SAP R/3 or ECC with respect to Logistics execution.
Time needed: 5 minutes
Steps to Configure SAP S4 HANA Logistics Execution Organization Structure in 5 Minutes
- Step 1-Define Loading Groups
Three Loading Groups (PA10-Manual Load, PA11-With forklift, PA12-With Crane) Created.
- Step 2- Define Transportation Groups
Two Transportation groups (PA10-Normal Transports, PA11-Special Car Carrier Required) Created.
- Step 3- Define Shipping Conditions
Shipping Conditions (P1-Standard, P2-Pick-up, P3-Immediately, P4-Transport Service, RE-Returns) Created.
- Step 4- Define Storage Conditions
Three Storage Conditions (P1-IM Managed Stock, P2-WM Managed Stock, P3-EWM Managed Stock) Created.
- Step 5- Define Shipping Point
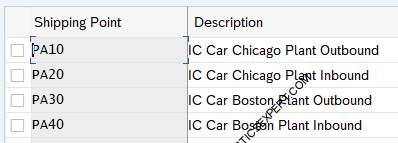
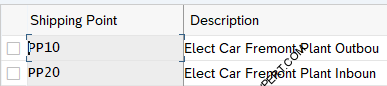
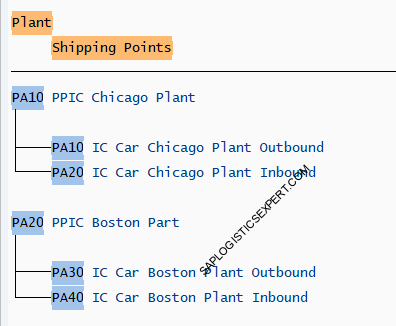
one Inbound and one outbound Shipping point is created for all three plants. So for Plant PA10, two shipping points as PA10-IC Car Chicago Plant Outbound, PA20-IC Car Chicago Plant Inbound. Similarly for plant PA20 & PP10 inbound & Outbound shipping point has been created.
- Step 6- Assign Shipping Point to Plant
Inbound & outbound shipping points created in above step are assigned to each corresponding plant
- Step 7- Shipping Point Determination
Shipping point determination is maintained as a combination of Plant*Loading Group*Shipping Condition
- Step 8- Determine Picking Location
Picking location determination configured as per rule “MALA” as Shipping Point*Storage Condition*Plant
- Step 9- Determine Good Receipt point
Inbound Shipping point is determined as a combination of Plant & Storage Location
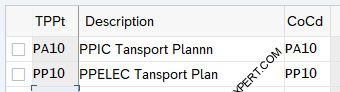
- Step 10- Maintain Transportation Planning Point
Two Transportation Planning points (PA10-PPIC Transport Planning Point, PP10-PPELEC Transport Planning Point Created)
Table of Contents
1. Logistics Execution (LE) Organization Structure in S4 HANA
Please see below all the components of SAP S4 HANA Logistics execution organization structure elements in pictorial form, which we will configure in this post.
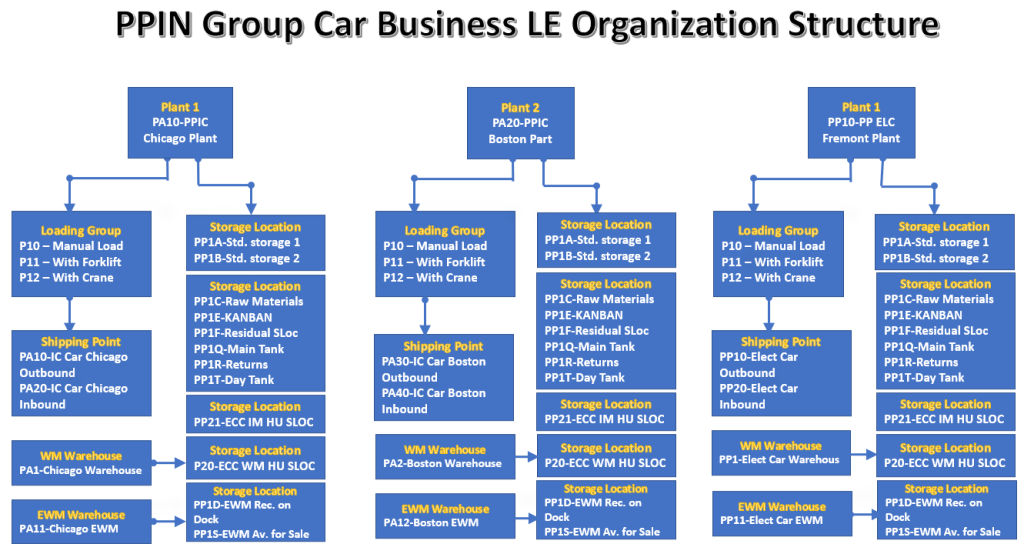
Before proceeding towards SAP S4 HANA Logistics Execution, organization structure , we need to understand the difference between Logistics execution in ECC and Logistics execution in S4 HANA
1.1 Logistics execution (LE) in SAP ECC
In SAP ECC business suite , Logistics execution is a combination of the below components
- Shipping
- Inbound Deliveries
- Outbound Deliveries
- Transportation (LE-TRA)
- Warehouse Management (LE-WM)
1.2 Logistics execution (LE) in SAP S4 HANA
SAP S/4HANA is successor of SAP R/3 and SAP ERP and is optimized for SAP’s in-memory database SAP HANA.
As SAP Business Suite 4 only runs on the SAP HANA database it is packaged as one product, SAP S/4HANA. While SAP’s classical R3, ERP and ECC based business suite and related products were designed to run on several database platforms, including those from Oracle, Microsoft and IBM.
1.2.1 Shipping in SAP S4 HANA
Shipping is not much change in S4 HANA. Sap S4 HANA also uses the outbound & inbound delivery and respective configuration same as SAP classic R/3 or ECC.
1.2.2 Transportation in S4 HANA
As per SAP simplification document, LE-TRA is not the target architecture within SAP S/4 HANA and the recommendation is to use Transportation Management (SAP TM). Even though LE-TRA functionality is still available within the SAP S/4 HANA, this is not considered as future technology. So basically TM replaces LE-TRA in S4 HANA.
1.2.3 Warehouse Management in S4 HANA
As per SAP simplification document, LE-WM is not the target architecture within SAP S/4 HANA and the recommendation is to use Extended Warehouse Management (SAP EWM). Even though LE-WM functionality is still available within the SAP S/4 HANA, this is not considered as future technology. So basically EWM replaces LE-WM in S4 HANA.
The earliest version of EWM till 2016 were only available as a decentralize EWM is on a separate server built either on on NetWeaver or SCM stack with any database. Then from 1809, decentral EWM is built on S/4HANA platform with HANA database.
from S4 HANA 1609 , an embedded version of EWM is also available within Sap S4 HANA.
You can read more on EWM on S4 HANA in detail HERE.
Note
Refer the post SAP HU vs HU to have a flavor of inbound & outbound delivery creation and process with respect to a HU mandatory Storage Location.
Refer the post Configure SAP S4 HANA Sales Documents in 10 Minutes to be familiar with the process of Outbound delivery configuration.
2. Configuration of LE Organization Structure
In this section we will configure all the components of LE organization structure one by one in detail.
2.1 Define Loading Groups
loading groups is defined here in the material master record for the sales data for each plant. Loading group is a mandatory entry to determine shipping points

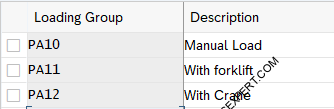
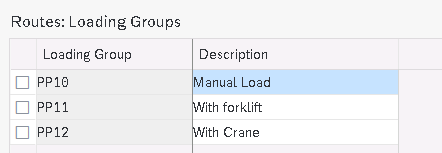
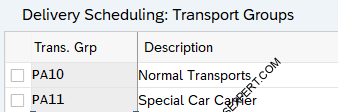
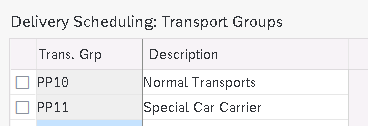
2.2 Define Transportation Groups
The transportation group is material specific which groups the material with similar requirements for transportation.
Note : Route is determined only if the transportation group is included in the material master as transportation group is a prerequisite for route determination
Created below transportation group for our companies
2.3 Define Shipping Conditions
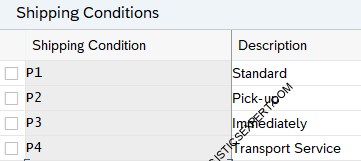
Define the conditions that need to be met for goods to be shipped. This is entered in customer master. Shipping point determination is carried out by the SAP system only if a shipping condition is contained in the sales document.
Note : We can also determine a shipping condition for each sales document type. This shipping condition is then used for determining the shipping point in the sales document instead of what is specified in the customer master record
Below Shipping Conditions are created for our car business

2.4 Define Storage Conditions
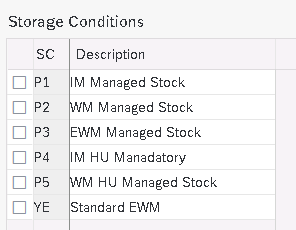
Define how goods should be stored. Storage conditions are entered in the material master record for each storage location.
Below storage conditions are defined for our car business

Below 4 Storage conditions are configured for our car business
- P1-IM Managed Stock
- P2-WM Managed Stock
- P3-EWM Managed Stock
- P4-IM Managed HU Required Managed Stock
- P5 -WM HU Managed Stock
So depending upon the material handling i.e. material is inventory managed or HU mandatory or Warehouse Managed or EWM managed , we will input storage condition in the material master
Now picking location is combination of shipping point * Plant * Storage conditions
2.5 Define Shipping Points
A shipping point is the top level in the organization for shipping. It can be allocated to several plants. and can be divided into several loading points.
The shipping point can be proposed automatically during order processing depending on the plant, loading group and shipping condition.

IC Car Shipping Points
Elect Car Shipping Points
2.5.1 Assign Transportation Zone to the Shipping Point
We need to assign transportation zone to our shipping points in order to determine the route
We have assigned transportation zone “0000000001-Region East” to all of our shipping points assigned to the plant PA10 & PA20 . For plant PP10 we have assigned transportation zone as “0000000002 – Region West”
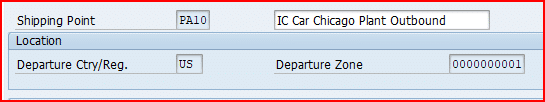
Note: Transportation zone in shipping point is used to determine the route. Please see the below post for details
2.6 Assign Shipping Point to Plant
We can allocate as many shipping points as desired to the plants. Any one shipping point can belong to several plants.
We have assigned shipping points to our respective car plants as below
IC Car Plants
Electrical car Plant
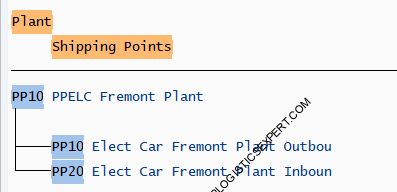
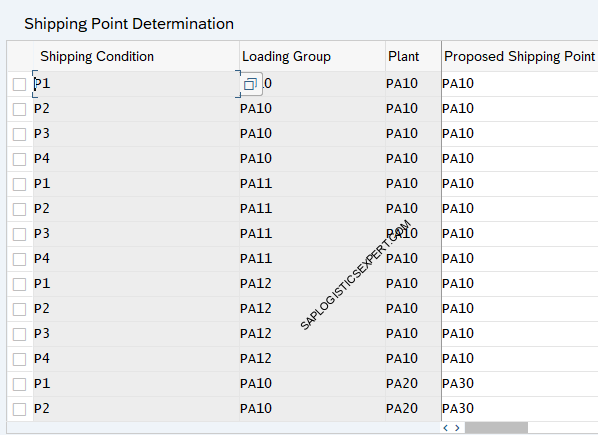
2.7 Shipping Point Determination
System allocates the shipping points to the desired combinations of shipping condition and loading group for each plant.
Note : Only Outbound Shipping Point has been configured here. There is a separate node for inbound shipping point configuration

Note
Shipping point determination in sales order/outbound delivery is mandatory in order for the system to be able to process the shipping process. Please click HERE to see the testing of determination of sales order at the time of sales order creation
2.8 Assign Picking Location
The picking rule defines how the system determines the picking location
Thee are two rules for picking location determination. We can not change them
2.8.1 Picking Rule “MALA”
MALA rule determine the picking location according to:
- Storage condition from the material master
- Delivering plant of the delivery item
- Shipping point of the delivery (see the section above on Shipping point determination)
We will use “MALA” picking rule
2.8.2 Picking Rule “RETA”
RETA rule is generally used in retail sector
- Storage location
- Delivering plant of the delivery item
- Situation
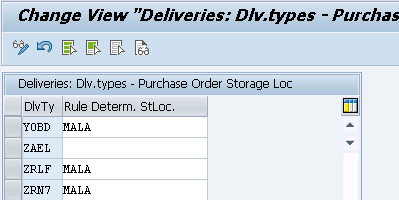
2.8.3 Assignment of Picking Rule
Picking rule is assigned to delivery type
for our car business, we have configured a customized delivery type “YOBD”
Please click HERE to check the detail of “YOBD” delivery type configuration
Let,s assigned the “MALA” picking rule to our delivery type “YOBD”
SPRO –> IMG –> Logistics Execution –> Shipping –> Picking –> Determine Picking Location –> Define Rules for Picking Location Determination
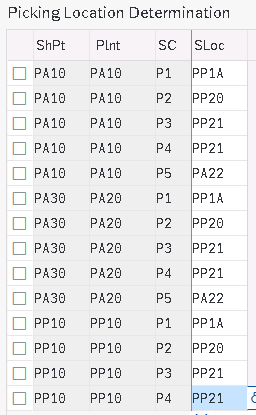
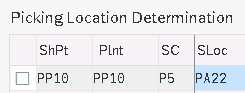
So as per rule “MALA”, we will assign the picking locations to the combinations of shipping point and storage condition for every plant.
Note : We will determine picking storage locations in outbound deliveries. Since we have all type of storage locations like Std Storage Locations, IM HU Managed SLOC, WM Managed, EWM Managed so we need to determine picking storage locations corresponding to storage conditions accordingly.
EWM Picking location in outbound deliveries will be “PP1S – EWM Available for sales” , which is different from EWM Inbound deliveries SLOC as “PP1D – EWM Receive on Dock”. The available stock is changed from PP1D to PP1S through EWM functionality of stock availability
- IM Picking -If a Material is managed in IM SLOC then IM Standard SLOC should be determined
- IM With HU Mandatory – If a material is managed in IM SLOC but HU is mandatory
- WM Picking – If a Material is managed in WM then WM managed SLOC should be determined
- EWM Picking -If a Material is managed in EWM then a EWM managed SLOC should be determined
- WM With HU Mandatory – If a material is managed in WM SLOC but HU is mandatory

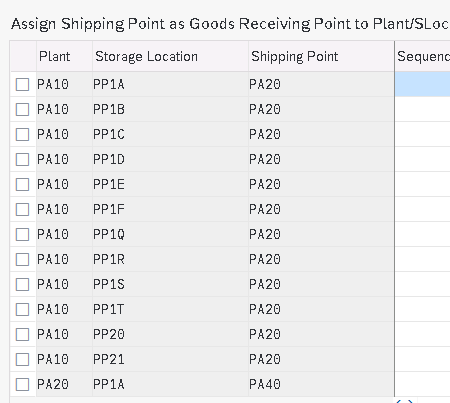
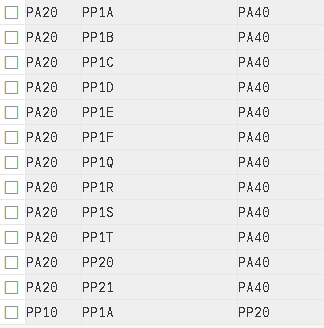
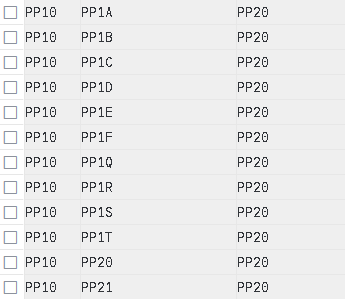
2.9 Assign Goods Receiving Points for Inbound Deliveries
Here we define the determination of inbound shipping point corresponding to Storage location.
Note : Storage location in inbound delivery depends on the SLOC given in Purchase Order Which comes from material master record. Here we will assign inbound shipping point corresponding to every Plant & every SLOC.
3. Maintain Transportation Planning Point
The transportation planning point is responsible for planning shipments

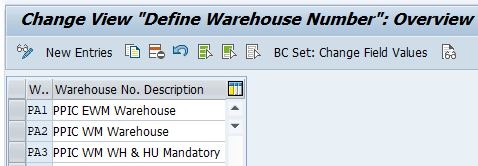
4. Define Warehouse Number
Here we will configure warehouses for our virtual car business.
For our car business we will use the below types of Warehouses --> EWM Warehouse --> WM Warehouse With SU Active --> WM Warehouse with Mandatory HU Active
We have defined below three SLOCs for these warehouses
- PP20-ECC WM SLOC
- PP22-ECC WM HU Mandatory
- PP1D-EWM WH Receive on Dock
- PP1S- EWM Available for Sale
Let’s define the warehouse now
SPRO –> Enterprise Structure –> Definition –> Logistics Execution –> Define, copy, delete, check warehouse number
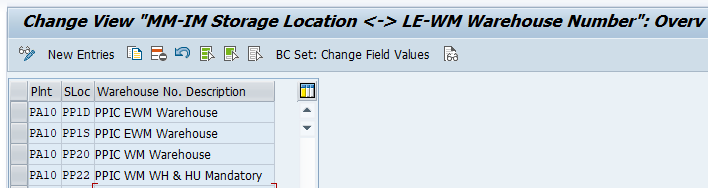
5. Assign Warehouse Number
We will assign these warehouses to the respective plant & storage locations as shown below
SPRO –> Enterprise Structure –> Assignment –> Logistics Execution –> Assign Warehouse Number to Plant and Storage Location
Logistics Execution Organization structure configuration ends here.
Since now we have configured All Modules Organization structure like FI (CLICK HERE), SD (CLICK HERE) , MM (CLICK HERE) & LE (in this post) now we can start creating Materials, Vendors & Customers and further scenarios (after activation of material ledger which is mandatory in S4 HANA)
Before Configuring LE Organization structure, we need to configure FI, SD & MM Org. Structures. Click on above link to see the minimum required FI, SD & MM Org.Structures
We have completed Minimum Required organization Structure. next step is to activate Material Ledger (Mandatory for S4 HANA). Click on the above link for more detail.
Image Courtesy : Man vector created by macrovector – www.freepik.com

