In this post we will configure full sale cycles for most widely used sales process. To configure SAP S4 HANA Sales Documents in 10 Minutes, we will focus mainly on standard sales order (to customers) & sales to other plants (through intracompany & intercompany STOs).
Time needed: 10 minutes
Component to configure SAP S4 HANA Sales Document in 10 Minutes
- Step 1 – Configure Sales Order Type
YOR-PPIN Std. Sales Order
- Step 2 – Configure Item Categories
Sales Item Categories-YTAN-Standard Item
STO Item Categories – YULN-Standard Stock Transport Item, YNLN-Standard Stock Transport Item, YNLC-Inter Co Stock Transport Item. - Step 3 – Configure determination of Item categories in Sales Order
It is a combination of : sales document type*Item Category Group*Usage*Item Category of height level Item
- Step 4 – Configure Schedule Line Category
YP-MRP, YV-Consumption MRP, YN-No Material Planning
- Step 5 – Configure schedule line Category Determination
It’s a combination of : Item Category * MRP Type from Material Master
- Step 6 – Configuration of Delivery Type
YOBD-Outbound Delivery CS, YNL-Replenishment Delivery, YNLC-Replenishment Cross-Company
- Step 7 – Configuration of Delivery Item Categories
Sales Item Categories-YTAN-Standard Item
STO Item Categories – YULN-Standard Stock Transport Item, YNLN-Standard Stock Transport Item, YNLC-Inter Co Stock Transport Item - Step 8 – Determination of Item Category in Delivery
It is a combination of : Delivery type*Item Category Group*Usage*Item Category of height level Item
- Step 9 – Configuration of Billing Type
YF2 – Invoice
- Step 10 – Copy Control : Sales Order (YOR) –> Outbound Delivery (YOBD)
Header Copy
Item Copy - Step 11 – Copy Control : Outbound Delivery (YOBD) –> Invoice (YF2)
Header Copy
Item Copy - Step 12 – Final config of flow YOR –>YOBD–YF2
Assignment of YOBD & YF2 to YOR
Table of Contents
1. Sales Order Type
Sales document types control the functioning of sales document. For example, a returns order to receive goods back from a customer will function differently than a sales order or a quotation.
The sales document is comprised of three general levels of data and control:
- The sales document header, which is controlled by the sales document type
- The sales document item, which is controlled by the sales item category
- The sales document schedule line, which is controlled by the schedule line category
We will configure our own sales document types to be used in full sales cycle YOR (order) --> YOBD (delivery) --> YF2 (billing).
We will configure our own, Sales Order type YOR.
1.1 YOR -PPIN Std. Sales Order
The sales document type controls the central header details of the sales order
Let’s focus on the configuration of our standard basic sales
order process to be used for our car business.
- The number assignment should be internal.
- Item numbering should have an increment of 10.
- Order entry should begin with the Item overview screen.
- Checking open quotations or contracts is not necessary.
- Billing document type F1– SAP Standard
- Requested delivery date to be proposed automatically with a lead time of 10 days.
- Pricing should be based on the current date.
- Automatically propose the current date as the customer reference date (Cust.Ref. Date) .

Configuration of Sales order type with minimum possible fields but we will explain all the fields
1.1.1 Explanation of all fields chosen for YOR Order Type
First we will explain all the fields given on the top areas (shown in below screenshot)
1.1.1.1 Fields in Main Header Area
There are total 4 fields in this area given below

a) SD Document Type
Give our customized name here . We have chosen YOR – PPIN Std. Sales Order
b) SD Document Category
The document category is C, meaning a sales order document type, rather than a quote, etc.
c) SD Document Block
The sales document is not blocked for processing so can be used by the business.
1.1.1.2 Fields in “Number Systems” Sub-screen
There are a total of 4 fields in this area .

a) No. Range Int.
Internal number range interval is 01.
b) No. Range Ext.
We have configured Ext no. range 02 for our order type.
c) Item No. Increment
The items in the sales order increase in increments of 10
d) Subitem Increment
the sub-items increase in intervals of 10.
1.1.1.3 Fields in “General Control” Sub-screen
Below fields are present in this area.

a) Item Division
The division of the material or item is not to be copied into the sales order.
b) Check Division
There is a check with an error message to see if this division is equal to the header division. for our YOR it will raise an error if it is not equal.
c) Probability
The probability of this order being completed and fulfilled is 100 percent.
d) Read Info-Record
The system must read the customer material info record, should one exist.
e) Check Credit Limit
The credit limit check field is blank, which means no check.
f) Enter PO number
Blank means -The system must not check the purchase order number for our “YOR” order type
g) Output Application
The output application is assigned for sales. We assigned standard V1 for our order
h) Commitment Date
The commitment date is not checked. The commitment date will be recalculated if changes are made to the material, quantity, requested delivery date, or delivery time.
1.1.1.4 Fields in “Transaction flow” Sub-screen
Below fields are present in this area

a) Screen Sequence Grp
The screen sequence group controls the way data is displayed, and in what sequence.
b) Display Range
The display range determines what items in the sales order are displayed—We have selected UALL All items
c) Function code for overv.scr
The function code for overview screens is the function code that determines what data and layout you see in the sales order—for example, item overview or item detail.
d) Incompletion procedure
We have selected std incompletion procedure “11” for our YOR Sales Document
e) Transaction Group
The transaction group determines what indices must be updated with reference to this sales order. “0” means order.
f) Quotation messages
For our order type since we have not configured quotation process so we have set as “Do not Check”.
HINT
Quotation messages and contract messages are set with an indicator B. Quotations, contracts, and master contracts are the three preceding key document types. So when you create a sales order you may want the system to give you a warning if open quotations exist. This setting B checks to see if the item is available on any other quotations or contracts for this Sold-to Party. Perhaps the user would then create the order with reference to that quotation or contract.
g) Doc. Pricing Proc.
At present we have defaulted “A” for our order type. We will input our customized value for this field after configuration of pricing procedure.
HINT
The document pricing procedure is this indicator plus the indicator on the customer master and the relevant sales area these determine which pricing procedure to use.
Note:
Please see the below screenshot after completion of pricing procedure. Please click HERE to check the pricing procedure configuration

h) Status profile
Status profile is used to assign a status profile to the particular document type. It is also assigned at item category level. For our Document type it is blank i.e. we have not assigned any.
i) Message: Mast.contr.
We have used blank means “Do Not Check”.
HINT
Message master contract checks to determine if any master contracts exist while you are creating a document type “contract.”
j) ProdAttr.messages
We have chosen “A -Dialog”
HINT
With product attribute messages, the system can error or warn to check manually entered products for the attributes to see if the Ship To party accepts them. In the case of automatic material entry, such as material determination, this check is ignored.
k) Incomplet.messages
With the incomplete messages indicator blank for our order type, the system will inform at the time of saving that the document is incomplete. However, we will still be able to save the document.
1.1.1.5 Fields in “Scheduling agreement” Sub-screen
The scheduling agreement area is used by scheduling agreement document types. Below fields are present in this sub-screen

a) Corr.delivery type
The correction delivery type is used for scheduling agreements. it is blank as we not configuring scheduling agreement.
b) Usage
This field is blank for our order type
HINT
The usage field is used to indicate on the sales order what the customer uses the
material for. This entry will be copied into all items, or it may be placed into items individually in the sales order.
c) MRP for DlvSchType
It is blank for our order type means Delivery schedules are not used.
HINT
MRP for delivery schedule type is used for scheduling agreements in order for them to set if the system should use just in time (JIT) processing or forward the demands on to material requirements planning (MRP).
d) Delivery block
Delivery blocks can be automatically set for scheduling agreements. A blank entry indicates no delivery block.
1.1.1.6 Fields in “Shipping” Sub-screen
Below fields are present in this subscreen

a) Delivery Type
This field indicates that this document type is relevant for delivery, and the delivery type to be used for automatic processing is LF.
HINT
At present we are giving SAP standard delivery type here, but later on we will swap it with our own delivery type.
b) Delivery Block
We have chosen blank means there is no automatic delivery block entered in the sales order.
c) Shipping Conditions
It is blank for our order type. Means for this order type shipping conditions are to be taken from customer master records.
HINT
The shipping conditions are proposed by the customer master record. Should an entry have existed in this field, this entry would have taken precedence and overwritten those found on the customer master record. The shipping condition value is used to determine the shipping point.
d) Immediate delivery
We have chosen blank means “Create delivery separately” i.e. we do not want immediate delivery for our order type.
HINT
The immediate delivery indicator is not set. This flag creates a delivery automatically immediately after saving the sales order. The delivery is not completed and the picking, packing (if relevant), and goods issue must still be carried out.
1.1.1.7 Fields in “Billing” Sub-screen
Below fields are present in billing sub-screen

a) Dlv-rel.billing type
This document is relevant for invoicing and for delivery-related invoicing, the system automatically uses invoice document type F2. We will change later this to our customized billing type.
b) Order-rel.bill.type
When an order-related invoice is possible the system will use document type F2 for automatic processing as well. (This makes sense if you wish your order and delivery relevant products to be invoiced at the same time.)
c) Intercomp.bill.type
The inter-company billing document type for automatic processing is IV.
d) Billing block
There is no automatic posting of a billing block on our sales order.
HINT
It may be necessary, however, to have a billing block for credit notes. This means that the order cannot be billed until the billing block is removed. Using a billing block is a safety feature. For example, you may have a background job that creates invoices. When you save the order, this background job will see the order and then invoice it if it is for order-related billing. Using the billing block will prevent this from happening until the order has been checked and the billing block explicitly removed.
e) CndType line items
We have assigned std “EK02”. The condition type for line items is used to determine the costing of the line item. It must be equal to the condition type allocated on your pricing procedure.
f) Billing plan type
It is blank for our order type as we are not using any billing plan.
HINT
The billing plan type is either periodic billing, where the entire value to be billed to date is billed in full on the billing plan date (for example, a rental agreement), or milestone billing, where the total value to be billed is distributed between the
individual billing plan dates (for example, for a project based on project milestones, where the value billed on each date can be a fixed amount or a percentage).
g) Paymt guarant. proc.
We used “01-Standard”
HINT
Payment guarantee procedure indicates to the system what form of guarantee procedure to use for this sales document. These are risk management.
h) Paymt card plan type
We used “03-Payment Card”
HINT
Payment card plan type is an essential setting should you want your system to accept payment cards in the sales order process.
i) Checking Group
We used “01-Standard”
HINT
Checking group is used to determine how the system carries out the checking of payment card data
1.1.1.8 Fields in “Requested delivery date/pricing date/purchase order date” Sub-screen
These settings affect the requested delivery date

a) Lead time in days
Lead time in days is the requested delivery date in the sales order. we have selected 10 days for our order type.
b) Propose Deliv.Date
The propose delivery date checkbox is checked to propose the current date as the delivery date. We have selected this for our order type.
c) Date type
Date type allows the user to set the format of the delivery schedule line date for internal system use—for example, date, week, month, etc. We have chosen 1 which is “Day”
d) Prop.f.pricing date
Proposal for pricing date allows you to specify the valid-from date for the pricing of the reference document, or the requested delivery date, or the current date. we have selected blank which means “Proposal based on today’s date”
e) Prop.valid-from date
Propose valid-from date allows you to determine when the valid-from date for pricing should be. This is used, for example, in quotations. We have chosen blank means “No Proposal”
1.1.1.8 Fields in “Contract & Availability Check” Sub-screen
Below are the fields in this sub-screen

Since we have not configured contract so we are skipping this last section
2. Item Category of Sales Documents
The sales item category is one of the most important fields in the SAP sales order. It controls the sales document flow and also impacts the schedule line category
Item Category realize different business processes for each item in the sales document.
Item Category decided below behaviour of the materials in the sales documents
- Relevance for billing of an item – The value determines what kind of billing document it has to generate for this item. That is order related billing document or delivery related billing document.
- Billing block – The billing block indicator is used to block each item of this category for billing.
- Pricing relevance – It indicates whether the system automatically carried out pricing for this item.
- Business data relevance item -It allows the business data at header level differs with item level business data.
- Schedule line allowed – It indicates whether we can create schedule lines for the item.
- Item relevant for delivery -It indicates whether a text or value item is relevant during delivery processing. The item itself is not delivered. But it serves only for information purpose in delivery documents.
- Returns – It indicates the item is return item
- Determine cost – This indicator enables the system to calculate cost of the material of this item category (condition type VPRS is used to calculate the cost price).
- Credit active – This indicator enables to configure credit management functions for this item.
- Incompletion procedure – We will configure Incompletion procedure in IMG and assign to item category. System reminds the end user if he does not maintain any values at item category level in the sales document.
- Partner determination procedure – This decides at item level and decides itself sold to party, ship to party, bill to party or payer for this item.
- Structure scope (relevant for bill of material explosion) – The value of this field determines whether the item is a BOM item. If it is so, how it should be exploded.
- Value contract material – The system copies value contract item that we specified here into the value contract.
- Contract release control – Here we can specify the system responses when the target value of value contract has been reached while releasing the contract.
We will configure below Item Categories for our car business sales documents. Second table is for purchasing documents (STOs)
| Item Category | Description |
| YTAN | Standard item |
| FREE | Free-of charge item |
| YTAP | Pric.at Item Level |
| YTAQ | Pric.at Header Level |
| TEXT | Text Item |
| YSER | Service |
| Item Category | Description |
| YNLN | StandStockTransItem |
| YULN | StandStockTransItem |
| YNLC | InterCo Stock Tr.Itm |
As we have decided earlier, we will configure first only most widely used sales process i.e. Sales to customer & STO.
Let’s first configure Standard item category for customer sales order.

2.1 Item Category YTAN-Standard Item

2.2 Item Category YNLC – Inter Company Stock Transport Item
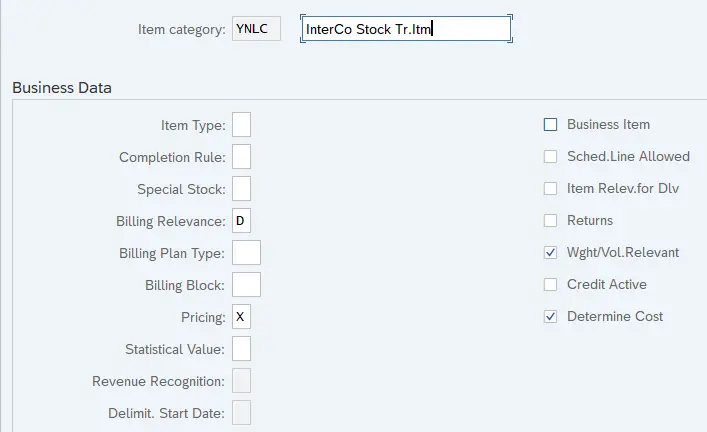
2.3 Item Category YNLN – Standard Stock Transport Item
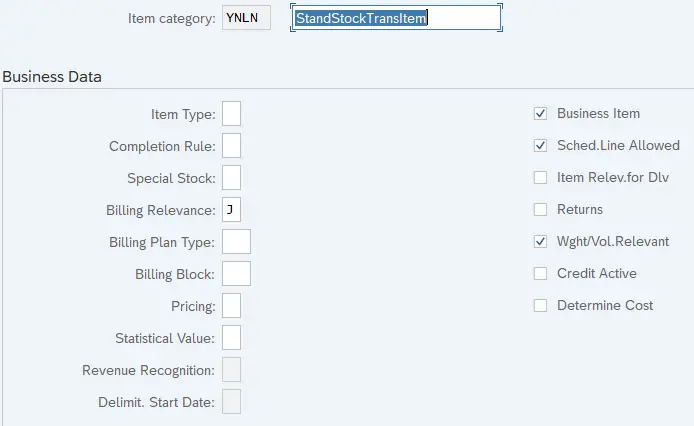
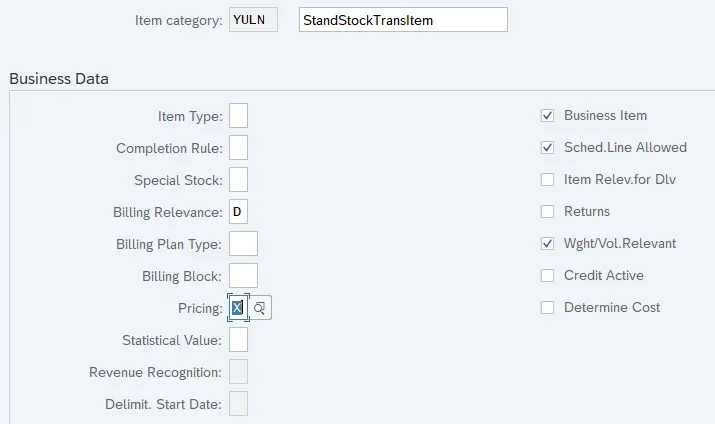
2.4 Item Category YULN – Standard Stock Transport Item
2.5 Item Categories to be used in the Inbound Deliveries
Please note that item category for inbound delivery needs to be maintained as a sales item category also, though item category will never have a sales order reference.
2.5.1 Reason of Inbound Delivery Item category configuration as sales document item category too.
For our car business inbound delivery, we will configure item category as “YELN”. We will define same item category key as “YELN” as a sales document item category also.
The reason for this is given below
--> Delivery item category key must be the same key as order item category. --> So we must define all delivery item categories as sales item categories in Sales and Distribution even for inbound delivery item category which is never found in sales documents. --> This is required for the system to create a copying relationship between the order and delivery document at the item level. For example DL/YELN to YEL/YELN.
2.5.2 Standard Inbound Delivery Item Category YELN
Standard inbound delivery items which will follow standard inbound process we will configure item category as YELN.
Below is the configuration of all fields for standard item category YELN


 Picture : Configuring Inbound Delivery Item category as sales document item category also Screen 2
Picture : Configuring Inbound Delivery Item category as sales document item category also Screen 22.5.3 Inbound Delivery Item Category for Spares YSPR
Since spares will follow a special inbound business process compare to the other standard line item of the standard inbound deliveries so we will configure a special line item category YSPR for spares.
We have configured YSPR as per below

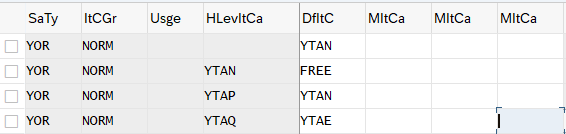
3. Item Category Determination in Sales Documents
Item category group field of the material master is the main factor to determine the item category in the sales order. This indicator + Sales document type + usage of the item category + Item category of higher-level item
decides the item category in the sales order document.
Item category is determined as per below combination in sales documents


We have configured our item categories as below
4. Schedule Line Categories
As we have seen in previous heading, An item category controls how the document item behaves. Each item is split into one or more schedule lines, which represents when the item will be delivered. For example, an order for 50 units may be delivered over 2 different weeks—25 units per week
As a connection to the inventory management, A movement type can be defined in the schedule line category.
--> Normal items are made delivery relevant at the level of the schedule line. --> Text & value items are made delivery relevant in the order item category.
Schedule line controls the below main functions
- Delivery Block – We can specify delivery block that the system applies automatically during processing. For example-free of charge deliveries as these documents have to be approved before processing.
- Movement type – Movement type for Inventory Management.
- Item relevant for delivery – If item is relevant for delivery.
- Req/Assembly – Requirements of sales document should be transfer to MRP by system automatically to create demand
- Availability – Availability check for materials and quantities in the sales order
- Product Allocation – To allocate products for customers evenly
Below schedule line are configured for our car business
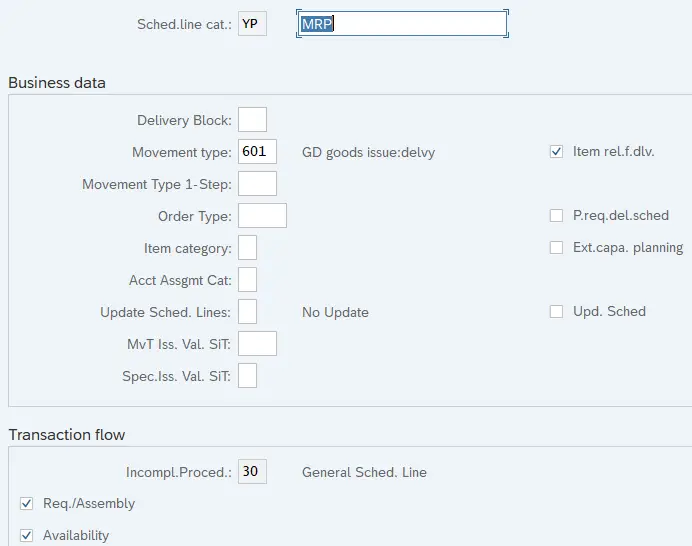
- YP – MRP
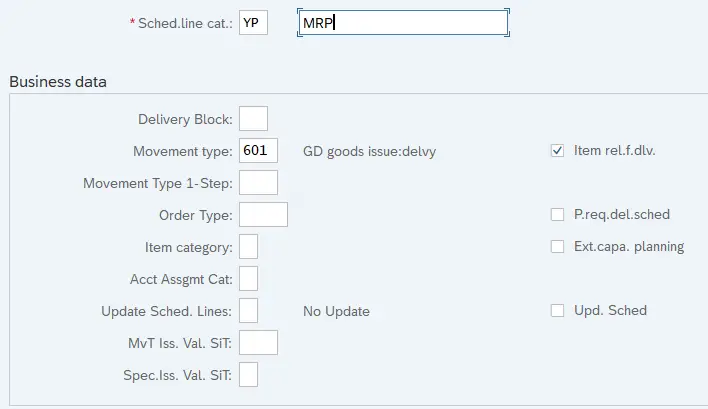
- YV – Consumption MRP
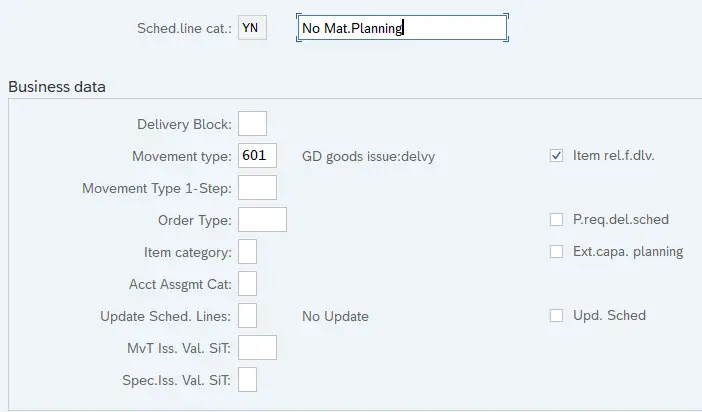
- YN – No Material Planning

4.1 YP -MRP
4.2 YV – Consumption MRP
4.3 YN – No Material Planning
5. Schedule Line Categories Determination
Schedule line category is determined based on the item category of sales order & MRP type from the material master.
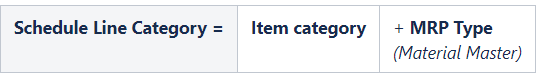

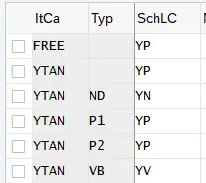
Note : MRY Types are SAP Standard. Below is the meaning of MRP type used
| ND | No planning |
| P1 | Forecast Consumption, Auto Firming, New Ords after PTF |
| P2 | Forecast Consumption, Auto Firming, No New Ords in PTF |
| VB | Reorder-Point Planning |
6. Deliveries in SAP
If our business is buying & selling then there are business documents like purchase order or sales order to specify what we purchasing or selling, at what price, on which date etc.
Since there are several activities (like picking/put away, packing etc.) between specifying buying or selling details (by Sales Organizations/Purchase Organizations) & actual delivery/supply of goods so there should be a connection between the purchaser order/sales order & actual receipt/delivery of goods. Deliveries fulfils this connection.
Deliveries in SAP specified by its direction . Deliveries related to inbound direction are inbound deliveries. Similarly deliveries related to outbound direction are inbound deliveries
Below are the main type of deliveries used in SAP and their respective preceding documents Sales Order --> Outbound Delivery Purchase Order --> Inbound Delivery Stock Transport Order --> Replenishment Delivery Subcontracting purchase Order --> Subcontracting Delivery
Let’s first have a common configuration to both inbound & outbound deliveries.
6.1 Delivery Type
We will define our delivery types which represent the different business transactions in shipping.
Delivery type configuration determines the below properties
- Document category [J] = Delivery-A classification for the different types of documents in sales and distribution Example : Quotations, Sales orders, Deliveries and Invoices.
- Item number increment: The increment by which item numbers is a sales, delivery or billing document to increase.
- Order required= Indicates whether a delivery that has no reference to an existing sales order is allowed.
- Default order type [DL] = Default order type for deliveries without reference to order
--> In the order type customizing , we define the delivery process and subsequent billing process that follows. --> But a delivery without any reference to real sales order, we have to define a default order type (DL here) in the Customizing for the delivery type. The Customizing for this default order type (DL) contains the default billing type for billing this delivery.
- Item requirement [202] = Requirement for item that does not refer to a sales order. It identifies a requirements routine for a delivery item that does not refer to a sales document.
- Storage Location Rule: It specifies how the system determines the picking location when delivery is created without entering a storage location for the items.
- Route determination : It specifies whether, during delivery processing, the system uses the route that is determined during sales order or whether it determines a new route.
- Delivery split Warehouse Number: It enables delivery spilt according to warehouse number
- Automatic packing: Automatic packing proposal is retrieved when a delivery is created. All items will be packed.
- General packing material item: This is used to allow generation of delivery items for packaging materials.
- Partner determination procedure : A grouping of partner functions. The procedure specifies which partner functions are allowed for a particular business transaction and which of those partner functions are mandatory.
- Distribution mode : To specify the time at which delivery is distributed to the decentralized WMS.
We will configure the below delivery type for our car business

6.1.1 Outbound Delivery
Outbound deliveries are created against sales order or against stock transport order from the sending plant.
We will configure all the main types of outbound deliveries one by one.
6.1.1.1 YOBD – Outbound Delivery Customer Sales
This delivery will be created based on sales order. We will configure our customized outbound delivery for customer sales



6.1.1.2 YUL – Delivery for Stock Transport Order

6.1.1.3 YNL – Replenishment Delivery

6.1.1.4 YNLC – Replenishment Cross-Company

6.1.1.5 YRL – Returns (Purchase Order)

6.1.1.6 YRLL – Return Del.to Vendor

6.1.1.7 YHOD – Outb.Deliv.GI Movement

6.1.1.8 YELR-Inter-Company Returns Delivery

6.1.2 Inbound Delivery
As name specifies, inbound deliveries are used for the goods direction inbound to our business.
Inbound deliveries are created based on the purchase orders and then further activities, such as packing, placing in storage, creating the warehouse order, and posting the goods receipt are done on the basis of inbound delivery
Delivery type for the inbound delivery is determined from the confirmation control. Please click HERE to see the details.
In addition to this there must be a default order type defined for the delivery type as we need customizing for order type. But for the deliveries which does not have any link to real sales order a default order type “DL” is defined.
This default order type "DL" uses the copy control “Order Type to Delivery Type” (i.e. from "DL" to "YEL") to transfer information from the purchase order to the delivery using the data transfer routine
6.1.2.1 YEL-Inbound Delivery for our car business
We will configure our customized inbound delivery type YEL for our car business.


6.1.2.2 YHID-Inbound Delivery HU Movement

6.1.3 YLB – Subcon Delivery

7. Defining Item Categories for Deliveries
Item categories are defined to have more control over individual materials in the deliveries. The item category is copied from an order item. A standard item in a standard order then becomes a standard item in the delivery. If a delivery is entered without reference to an order, the system proposes the item category depending on the delivery type and the item category group of the material.
Some Rules of Delivery Item Categories
--> When a sales order item is copied to a delivery, item category of the order item is copied to the delivery item. If order item or the schedule line assigned to order item is relevant for delivery a corresponding item category must be defined for the delivery.
--> Delivery item category key must be the same key as order item category. So we must define all delivery item categories as sales item categories in Sales and Distribution even for inbound delivery item category which is never found in sales documents. This is required for the system to create a copying relationship between the order and delivery document at the item level. For example DL/ELN to EL/ELN.
--> For all delivery item categories other than SD document category 7, a schedule line categories consisting of movement type must be determined in sales & distribution.
--> Delivery item category with SD document category 7 can be specified with movement type directly in delivery item category.
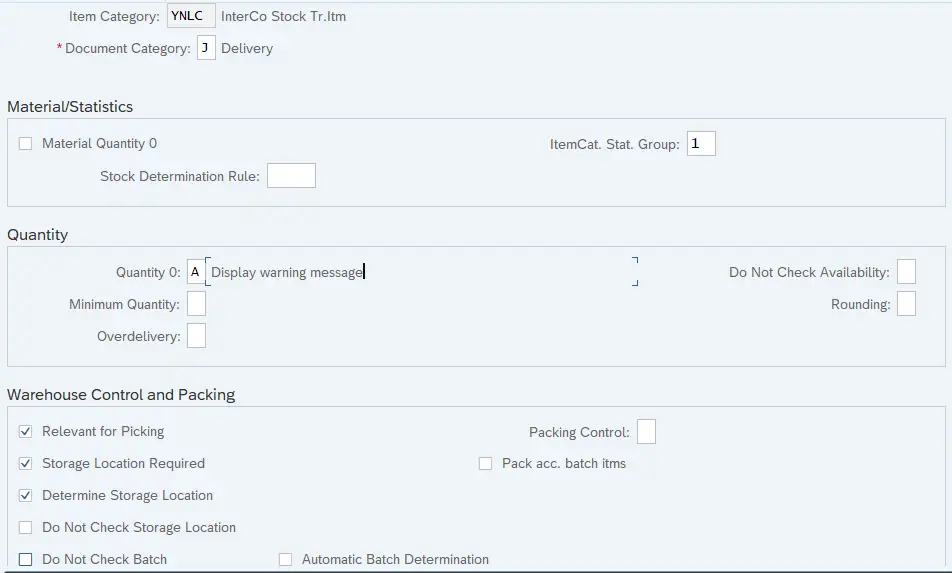
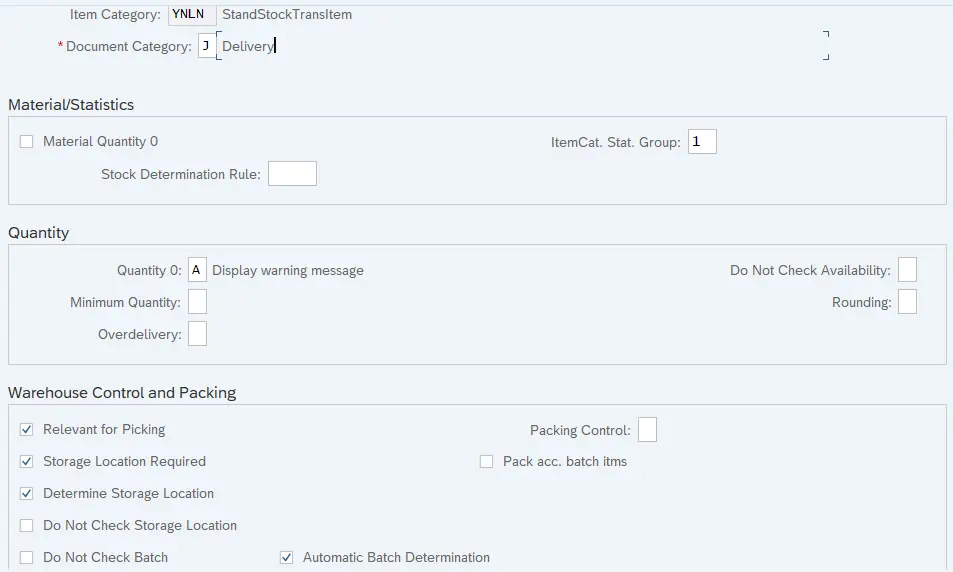
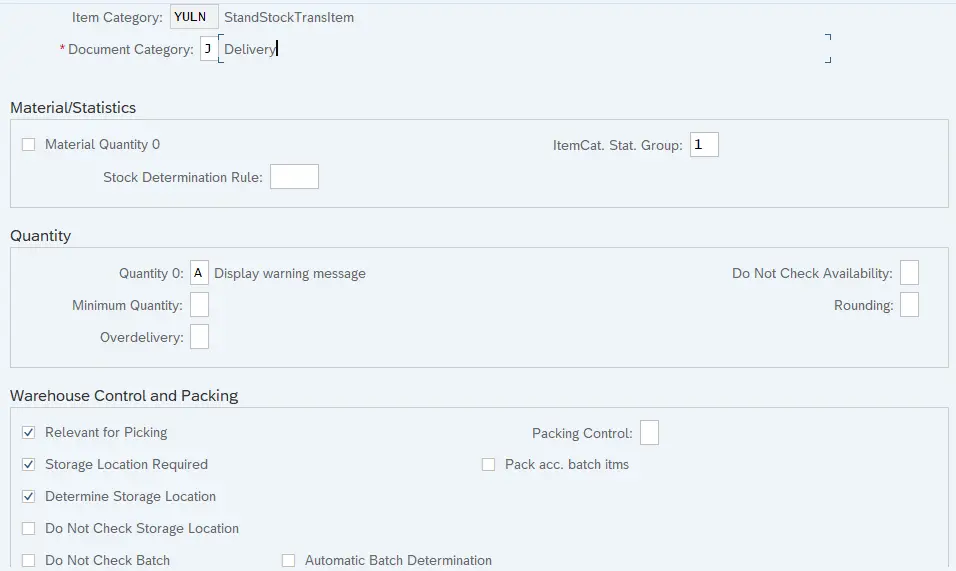
Delivery Item Category configuration determines the below properties
- Document category : A classification for the different types of documents in the sales and distribution system
- Material number 0 allowed: It controls whether it makes sense to enter an item with this item category without specifying a material. It allows to create a delivery document for a line item with 0 quantity, Ex-Text Item.
- Item category statistics group: It specifies a statistics group for this item category and helps determine which data the system updates in the Logistics Information System.
- Stock determination rule: Stock determination rule and stock determination group are combined into one key for stock determination strategy. This is used in the repetitive manufacturing process.
- Check quantity : It specifies when we create an item that has a 0 quantity, how system should give message. It is useful for the items that are creating without order.
- Check minimum quantity : It specifies whether system has to check minimum delivery quantity as per customer material info/Material Master record. System gives warning or error message.
- Check over delivery : It specifies how the system reacts whether warning or error message during delivery processing when original order quantity exceeds delivering order quantity as per info record.
- Availability check off : It is the control to switch on/off availability check for delivery items.
- Rounding : This indicator specifies rounding rules for whole number unit of measure. It is useful for BOM items.
- Relevant for picking or put away: It indicates whether item of this type are relevant for picking or put away. In the outbound delivery process, only delivery items that are relevant for picking are transferred to the warehouse management. Service items and text items are not transferred to the warehouse.
- Storage location required: This indicator makes storage location as mandatory in the delivery document.
- Determine storage location: It indicates whether system has to determine storage location automatically.
- Do not check storage location: It indicates whether system should run a check for the storage location that was determined.
- No batch check: It specifies system checks the batch number that entered in the delivery document.
- Packing control: It indicates whether delivery items with this item category:
- May be
- Cannot be
- Must be packed
- Pack accumulated batch items: It specifies if for a batch material only the main item with accumulated batch quantity is to be packed in the delivery, or if only items in which the batch is recognized can be packed. Example -if total quantity is 20000 but it is manufactured in 20 batches, then all those 20 batches appear to be packed i.e. 20 line items of the same material to be packed. Through this indicator we can pack only 1 line item that is the sum of all the 20 batches, so that packing can be carried out more efficiently.
- Automatic batch determination: This indicator enables to determine batch automatically in the delivery documents.
Below Delivery Item categories are created for our business
7.1 Item categories for Outbound Deliveries
Below item categories are configured for the outbound deliveries

We have customized a specific standard item category for our car business i.e. “YTAN”
Let’s configure standard item category “YTAN” first
7.1.1 YTAN -Standard Item

7.1.2 YNLC- InterCo Stock Tr.Itm
7.1.3 YNLN- Standard Stock Transport Item
7.1.4 YULN- Standard Stock Transport Item
7.2 Item Categories for Inbound Deliveries
As stated before, for our car business we are defining item category for inbound delivery as “YELN”
7.2.1 YELN – Item Category for Inbound Delivery
Let,s configure “YELN” for inbound deliveries for our car business.

7.2.2 YSPR – Item Category for Inbound Delivery for spares
We have configured a special line item category for spares materials which will follow a special business process compare to the standard materials.
below is the configuration of YSPR line item category

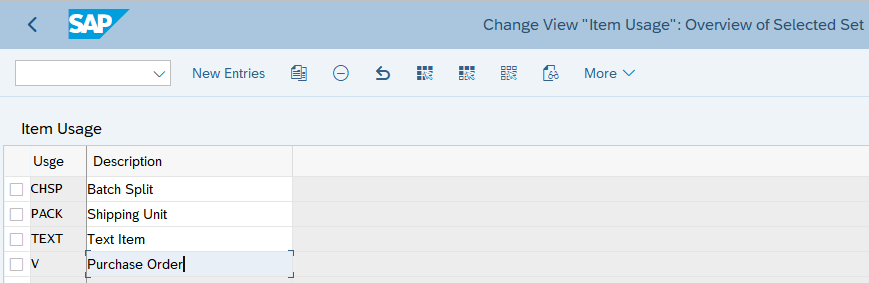
8. Define Item Category Usage
In this configuration, we specify the item category usages that control the usage of the item

9. Determination of Item Categories in Deliveries
There are two ways of item category determination in deliveries
- Process where item categories are copied from the higher level sales order item. For example- Sales order to outbound delivery.
- For order-independent items in the delivery like packing material, or inbound deliveries. no item category can be copied from a sales order. In this case in addition to the delivery type & item category group from the material master, a special functionality called “usage” is also taken into account.
- Some example of usage -PACK for packing items, CHSP for batch split & V for for inbound deliveries for purchase orders and for deliveries in STOs.
Please note that in material master there are two fields. One is "General Item Category Group" which is at MARA level. This field is used for inbound deliveries The other field "Item Category Group" is used with sales organization & distribution channel in deliveries.
We will configure item category determination for normal customer outbound delivery, intra-company STOs outbound deliveries, intercompany STOs outbound deliveries & inbound deliveries.
below is the path to determine item categories in deliveries.

9.1 Determination of Item Categories in Outbound Deliveries
For our car business, we have configure determination of Item Categories in Outbound Deliveries as below

9.2 Determination of Item Categories in Inbound Deliveries
We will configure the determination of Item Categories in Inbound Deliveries for all the business scenario
9.2.1 Item Category Determination in Standard Inbound Delivery
Below is the configuration of Item Category Determination in Standard Inbound Delivery

9.2.2 Item Category Determination in Special Process Inbound Delivery
Spare parts materials will follow a different process in inbound so we have configured a specific line item category YSPR for spare parts.
Below is the configuration of Item Category Determination in Special Process Inbound Delivery for spares

--> In the above item category determination different is the only Item category which comes from the material master. --> To determine different line item category "YSPR" for the spare parts materials from the the standard line item category "YELN", we have to input different "item category" in the material master of spare parts materials. Please check the below link to see this in detail 2 Minutes Guide to Create your First Material in S4 HANA-“Gen. item cat. grp” for Spare Parts Specific Business Purpose
10. Billing
10.1 Important configuration in Billing Type
- Transaction group : A group that allows you to control certain features of transaction flows by sales, shipping and billing documents.
- Billing category : It is used to differentiate the billing documents.
- Document type : This field classifies accounting documents. As invoice generates FI document type RV (Billing data transfer)
- Negative posting : Negative posting for same period.
- Branch/Head office: The indicator controls, which partner functions of the billing document, can be forwarded to financial accounting.
- Credit memo with value date : If the field is set, the reference billing document is not settled and the payment deadline date for the base billing document comes after the billing date for the credit memo.
- Invoice list : Classification that distinguishes between invoice list types that require different processing by the system.
- Posting block: it blocks automatic transfer of the data from invoice to FI document. Invoice has to be released manually then.
- Statistics: the value of the billing document is going to be updated in LIS. It indicates whether the system stores information from billing documents for the purposes of statistical analysis.
- Rebate settlement : If indicates whether the billing type is used exclusively during rebate processing.
- Relevant for Rebate: This indicator is one of the pre – requisite to process rebates.
- Cancellation billing type : It specifies the default cancellation for this billing type.
- Copying requirements : The routine checks that certain requirements are met when one document is copied into another.
- Reference number : The reference number is a piece of additional information forwarded from SD and FI.
- Allocation number : item that is forwarded from SD to FI. If you do not make an entry and the field is not filled in the order, the field remains empty.
- Account determination procedure: It specifies the condition types that the system uses for a particular type of document (Ex: Invoice) to determine the G/L Accounts to which amounts should be posted.
- Document pricing procedure : The key that specifies the pricing procedure for this type of sales document. The pricing procedure determines how the system carries out pricing for a particular sales document.
- Account determination reconciliation account: If a G/L Account is determined here, then the reconciliation account stored in the customer master record is ignored.
- Account determination cash settlement : It determines the condition types that the system uses to determine G/L Account for cash settlement. If this field is filled, then the billing document is not posted on the debit side. In this case the G/L Account determined is posted.
- Account determination pay cards : It specifies the condition types that the system uses to determine general ledger accounts for document types used in payment card transactions.
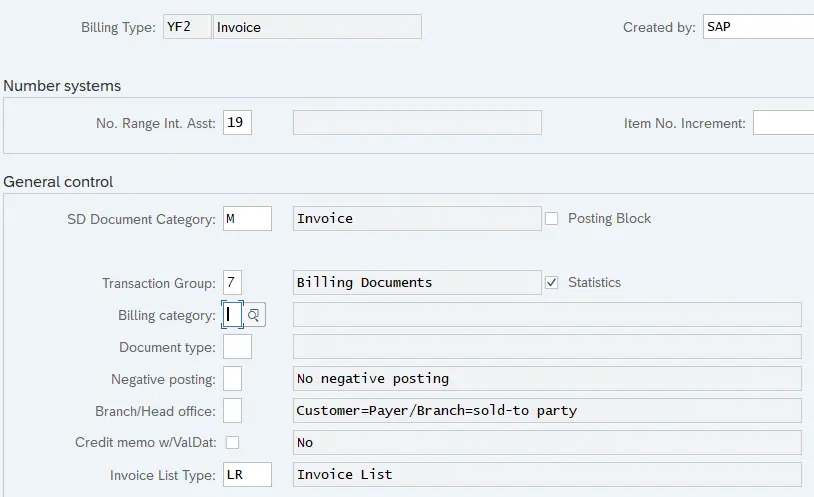
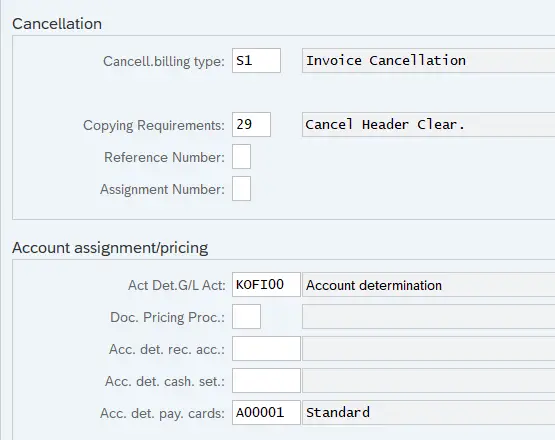
10.2 Configuring our Billing Type YF2
We will configure our own billing type “YF2” as shown in the below screenshots.
Note
Once we have configured our own Account determination procedure. We will assign this to the billing type YF2
Please check below post to have a step by step overview of the Account determination procedure
SAP SD FI Integration and Account Determination
11 Copy Control
We will maintain copy control for our Our flow YOR –> YOBD –> YF2
11.1 Maintaining Copy Control for Sales order to Delivery

11.1.1 Header Data Copy
We will first maintain copy control to copy header data
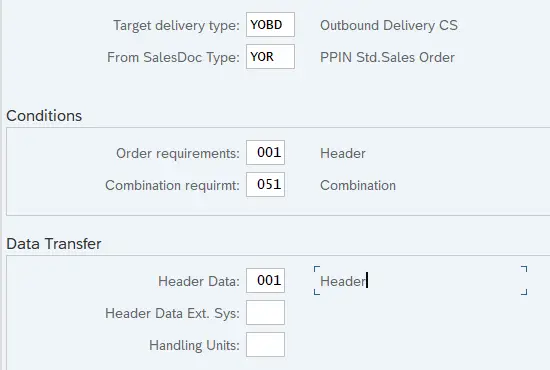
11.1.1.1 Copy Control for YOBD –> YOR
Please maintain copy control as per the screenshot shown below
11.1.2 Item Copy
Now we will maintain copy control to copy Items
11.1.2.1 Copy Control for TAN Item Category (YOR –> YOBD)
Please maintain copy control as per the screenshot shown below
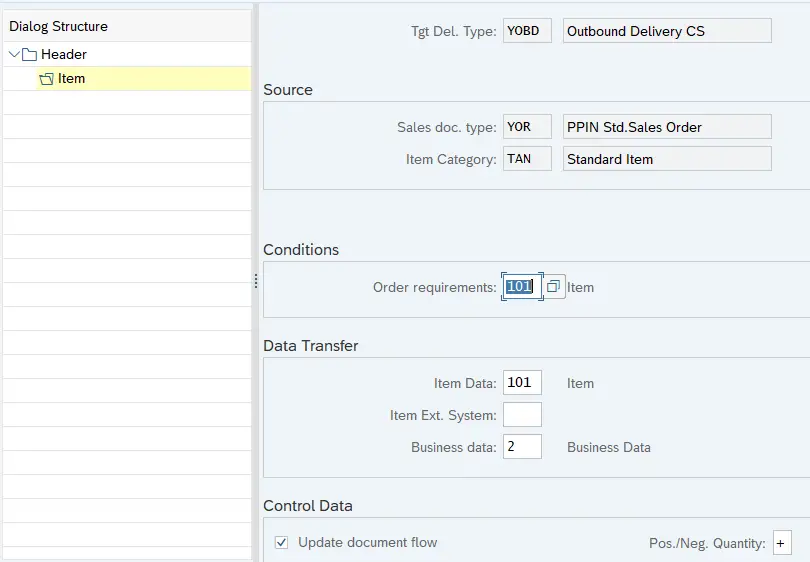
Since for our standard sales order “YOR” & outbound delivery “YOBD”, we have configured a specific item category “YTAN” instead of system standard “TAN” so we need to main copy control to resolve the copy control error shown HERE
11.1.2.2 Copy Control for YTAN Item Category (YOR –> YOBD)
Please maintain copy control as per the screenshot shown below

11.2 Copying Control: Delivery Document to Billing Document

11.2.1 Header Data Copy
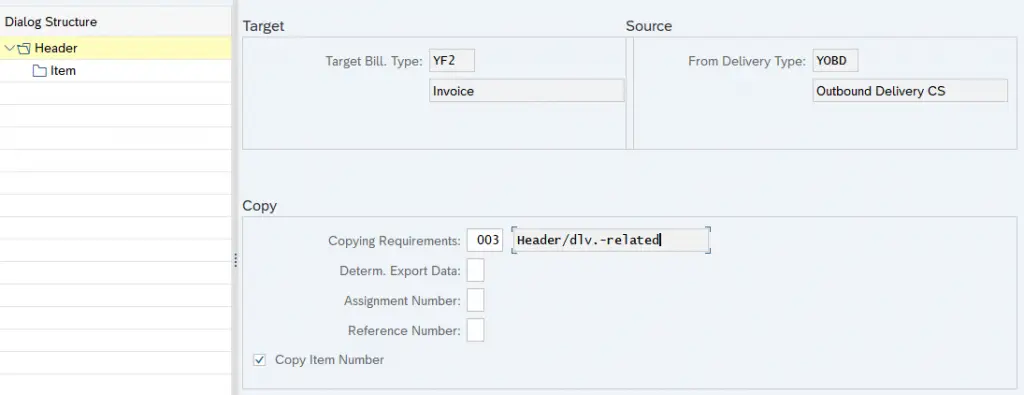
11.2.2 Item Data Copy
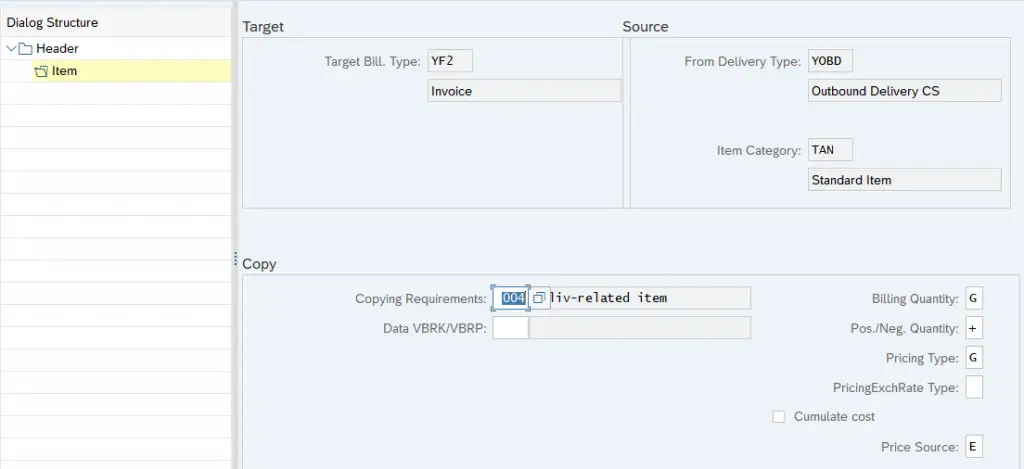
We have completed all the required sales documents.
11.3 Copy Control for Inbound Delivery
For inbound delivery we need to maintain copy control from default order type “DL” to our delivery type “YEL”


12. Final config of flow YOR –>YOBD–>YF2
Sine now we have configured our customized sales order type (YOR), outbound delivery (YOBD) & Billing (YF2). Let’s assign them as required to complete the flow
12.1 Assignment of YOBD & YF2 to YOR






