Handling Unit and bar codes goes into hand in hand in SAP S4 HANA. Before we go to SAP S4 HANA Handling unit vs Storage Unit in detail, let’s look at some of the basics of relationship between Handling unit & bar codes in SAP S4 HANA.
Table of Contents
1. What is Barcode
Bar codes are machine-readable codes in the form of numbers and a pattern of parallel lines of varying widths, printed on a commodity and used especially for stock control. We Observe barcode everywhere now a days. Barcodes represents GTIN (Global Trade Item Number)
2. GTIN (Global Trade Item Number)
The Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) is an Identifier of trade items. GTINs may be eight, 12, 13, or 14 digits long.
3. Types of GTIN
GTINs may be eight, 12, 13, or 14 digits long. The choice of barcode will depend on the application; for example, items to be sold at a retail establishment could be marked with EAN-8, EAN-13, UPC-A or UPC-E barcodes
3.1 GTIN-8/EAN-8
Used for small products scanned at point-of-sale (POS)
3.2 GTIN-12/UPC
GTIN with 12 digit. Typically assigned to products sold in the US
3.3 GTIN-13/EAN-13
GTIN with 13 digit. This is the most common Barcode/GTIN Type. It can be read at point of sale (POS) all over the world
3.4 GTIN-14
Groupings of trade items not intended for point-of-sale scanning. It is great for printing on cardboard when no extra information is required
3.5 GS1-128/EAN-128
If you need to encode variable information, such as best before or expiry dates, or batch numbers on your product, you’d use this one. So, it’s great for cases of short-shelf-life products and pallets. However, it can’t be scanned at point of sale. SAP Handling units (HU) uses this type of coding.
4. GTIN in Global Supply Chain
A product is represented through several units in the global supply chain. Below is the example in pictorial form to understand this better.
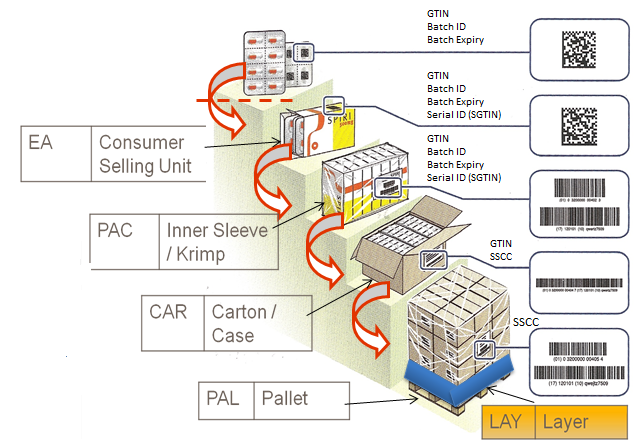
5. Units in Global Supply Chain
on a broad level there are three types of units in global supply chain
5.1 Consumer Units
Scanners at the retail point of sale are designed to read EAN-13, UPC-A, EAN-8 and UPC-E barcodes. Mostly EAN- 13 barcodes are used on their products. EAN-8 barcodes are used for very small products.
5.2 Traded Units
Scanners in warehousing and distribution and at the wholesale point of sale are designed to read EAN-13, UPC-A, ITF-14 and GS1- 128 barcodes, so one of these must be used.
5.3 Logistics Units
Scanners which are used to read labels on logistics units are designed to read GS1-128 barcodes. All the barcodes on the pallet label must be GS1-128 barcodes.
If the traded unit has to be barcoded with extra information, such as a batch number or variant number, use a GS1-128 barcode to encode this information together with the GTIN. For Example – SAP Handling unit label displaying Material number, quantity, Batch number etc along with SAP Handling Unit number.
6. GS1-128 Shipping Labels
GS1-128 shipping labels are logistic labels which enable shipment visibility within a supply chain. This commonly used to host the SSCC-18 barcode, which is used as a ‘license plate’
The primary purpose of GS1-128 Shipping Labels is to identify a shipment with data being received and transmitted by EDI. Specifically, fields such as the Purchase Order, Ship To Location and sometimes item information is received in the PO and are on many GS1-128 Shipping Labels. Each shipment has a supplier assigned license plate (SSCC-18) which is transmitted in the ASN.
7. SAP HU -> SSCC Generation Acc. to EAN128
In SAP we can configure
- How a bar code is constructed to print on SAP handling unit label.
- What information it should display.
For Example- For our Car business we want the below information to appear as a bar code on an EAN128 label in the below given sequence.
- EAN/UPC code
- Expiration date
- Quantity
- Serialized Shipping Container Code (SSCC)
- Variant
- Batch Number
The label is too narrow for the information to fit in one line, so the data must be split up into two lines.
7.1 Application Identifier (AI)
Each information to be displayed on HU Label is identified through Application identifier. We will display the above information on our EAN128 label through below application identifier
| Application Identifier (AI) | Description | Data Format |
| 02 | EAN/UPC/GTIN of contained item | 14 numbers: 13 digits + Check digit |
| 17 | Expiration Date | 6 digits: YYMMDD |
| 37 | Number of Units Contained (qty) | 1-8 digits |
| 00 | Serialized Shipping Container Code (SSCC) | 18 numbers: 17 digits + check digit |
| 20 | Product Variant | 2 digits |
| 10 | Batch Number | 1-20 alphanumeric |
Our EAN128 label will look as below

7.2 Configure in SAP for information to be displayed on EAN128 Lebel
Below is the path to configure this
Logistics General –>Handling Unit Management –>Basics –>Define EAN128 –>Define Bar Code Profile for Label
Define EAN128 Profile
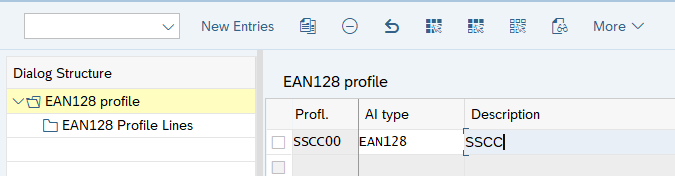
Select the Profile & Click on “EAN128 Profile Lines”
Now input application identifier corresponding to the information to be displayed line wise.
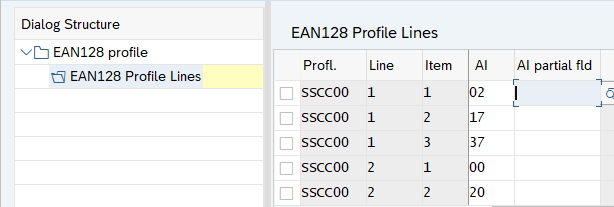
First, give this profile a unique name. Then
- In line one, assign AI 02 (EAN) to item 1, AI 17 (Expiration Date) to item 2, AI 37 (quantity) to item 3 and AI 15 (expiration date) to item 3.
- In line two, assign AI 00 (SSSC/HU Number/EAN128) to item 1, AI 20 (Product Variant) to item 2 & AI 10 (Batch Number) to item 3.
This profile then results in the following bar code.

FAQ on SAP Handling Units Practical Usage
Smallest consumer unit is denoted by BUOM in SAP , for Example- 25 gm packet of potato chips, 1 leaflet of tablets etc. You can input EAN type and EAN/GTIN code for each BUOM in Material Master data Basic data 1 view and in Additional Data view. This can be later printed on EAN128 label used for Pallets.
There are different types of barcodes used on different type of packaging like -GTIN-8/EAN-8 , GTIN-12, GTIN-13/EAN-13 & EAN128 etc. Different type of traded unit like cartons & pallets are represented by Handing Units in SAP.
Each transactional information is represented by Application Identifier (AI). For example -AI 02 represent EAN, AI 17 represents Expiration Date, AI 37 represents quantity etc. AI number 00 represents HU number. HU number is incorporated in the overall label information in the form of AI number 00.
Further Reading
Please check the below link to read further on Barcoding & GTIN
Global Trade Item Number – Wikipedia
GS1 UK | The Global Language of Business


